Frontier of Science and Technology | Analysis on the Index of Holographic Portrait of Road Network Structure for 36 Major Cities in China
Original Zhu Xinyu Dai Shuai Liu Jinguang Road Traffic Management Magazine included in the collection # 1 Science and Technology Frontier # 1 Holographic Portrait of Road Network Structure
Editor’s Note: A scientific and reasonable urban road network structure is an important foundation for ensuring road traffic safety, maintaining road traffic order and improving road traffic capacity. In order to solve the problem of lack of in-depth research on the basic theory of road network structure in China, with the support of the basic research project "Research on Urban Road Network Portrait and Traffic Control Technology Based on Big Data" (No.11104100000180001210102), the Road Traffic Safety Research Center of the Ministry of Public Security pioneered the holographic portrait model of urban road network structure. This paper makes a concrete, subtle and intuitive quantitative analysis of road network from the aspects of road network connectivity, road grade matching, intersection shape and lane grade, and puts forward a number of quantitative indicators such as road network connectivity, 100-kilometer broken road, intersection shape, intersection spacing, intersection level difference, access level difference, high/expressway entrance and exit spacing, road linear curvature gradient and so on, and makes an all-round analytical portrait of urban road network. This research is the first at home and abroad after novelty retrieval by authoritative organizations. Since the beginning of this issue, this journal will publish articles one after another to introduce the holographic portrait model of urban road network structure in detail. In this issue, firstly, the connectivity index of urban road network in the model is interpreted.
I. Connectivity index of urban road network
Connectivity in English is a topological property of space or set. Urban road network connectivity refers to the density of intersections in urban road network and the direct degree of road connection. At present, it is generally believed that road network connectivity refers to the index that represents the interconnection between roads on the basis of a certain road network density. This index can reflect whether there are many broken roads and T-junctions.
A highly connected road network has many advantages for urban traffic and people’s travel. A highly connected environment can provide more direct roads to shorten the distance to the destination. A highly connected road network can reduce the traffic volume of main roads, make room for emergency vehicles, reduce the cost of public facilities connection and services, improve the average speed of the road network, reduce traffic congestion and reduce the probability of traffic conflicts, thus avoiding traffic accidents.
There are many methods to calculate the connectivity of road network, and these metrics are different because of different measurement methods. After synthesizing many calculation methods at home and abroad, this study adopts the connectivity index of road network generally recognized in China to reflect the connectivity level of urban road network.
Second, the calculation method of urban road network connectivity
Urban road network connectivity represents the quantitative degree of road network connectivity. The higher the value, the better the connectivity. If the density of road network is constant, the higher the connectivity of road network, the more reasonable the structure of road network is. There are two calculation methods for urban road network connectivity, as shown in Formula 1 and Formula 2.

Where: j is the connectivity of road network; N is the total number of nodes in the road network; Mi is the number of edges adjacent to the ith node; M is the total number of edges (number of road sections) of the network.
The types of urban road networks in China are mostly grid-shaped, and the connectivity of grid-shaped road networks increases with the increase of nodes, and gradually approaches 4. At the same time, under the same number of nodes, the connectivity of intersection is better than that of T-junction, and the fewer broken roads, the higher the connectivity.
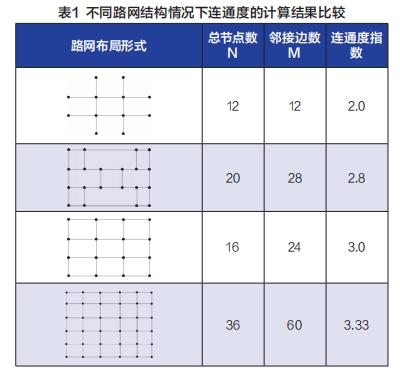
Third, the actual measurement results of connectivity of 36 major cities in China
Based on the above connectivity calculation model, this study measured the actual road network of 36 major cities in China. Firstly, the built-up area and regional scope of the city are determined by remote sensing images. Secondly, the overall connectivity index of each city is calculated by navigating the actual road network vector information of the electronic map, and the following conclusions are drawn.
(A) China’s 36 major cities’ road network connectivity index is generally low.
The theory and application of urban traffic planning puts forward that the road network connectivity index of small and medium-sized cities should be between 3.2 and 3.5, and that of big cities in China should be between 3.6 and 3.9. However, according to the measured data, the connectivity of road networks in 36 key cities in China is between 3.2 and 3.4. Compared with the reasonable connectivity value of 3.6 to 3.9, the connectivity of road networks is generally low.
(B) large-scale urban road network connectivity is high.
The researchers divided 36 big cities according to the city size, and found that the connectivity of large-scale urban road networks was generally high. The average road network connectivity of megacities and megacities is 3.29 and 3.31, respectively, which is generally higher than the average road network connectivity of type I and II megacities of 3.27 and 3.26, as shown in Figure 1.
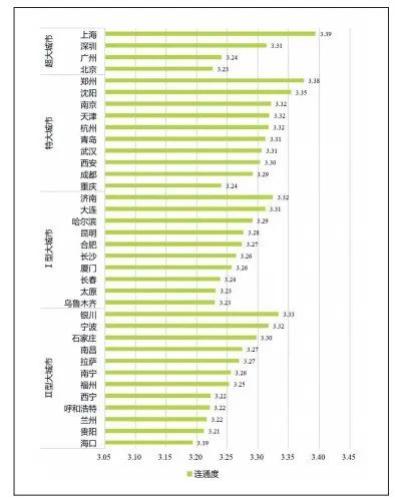
Figure 1 Distribution of Road Network Connectivity in Cities of Different Sizes
(C) The connectivity of urban road network has a strong correlation with the overall urban form.
According to the overall form of urban road network structure, the researchers divided 36 key cities into "cluster, group and strip". Among them, cluster-like refers to the "cake-spreading" road network with concentrated urban road network structure and radial and annular intersection from inside to outside; Group-like means that the urban road network structure is blocked by mountains, rivers, lakes and seas, so that the urban area presents a number of scattered group-like road networks of different sizes; Strip-like road network refers to a strip-like road network, which is limited by topography and can only be developed in narrow valleys or basins.
According to the measured data of 36 major cities, the connectivity of urban road network in cluster form is high, while that in cluster or strip form is relatively low. Cluster cities, such as Beijing, Shanghai, Chengdu and other 16 cities, are located in plain areas, and the development of urban road network is not limited by topography. The urban trunk road network is composed of horizontal and vertical roads and circular roads, which generally has good connectivity; Group cities, such as Guangzhou, Shenzhen and Hangzhou, and strip cities, such as Xining, Lanzhou and Lhasa, are limited by geographical conditions. Because cities are often divided by water systems or mountains, it is difficult to build urban trunk road networks, and the connectivity of road networks is generally low, as shown in Figure 2.
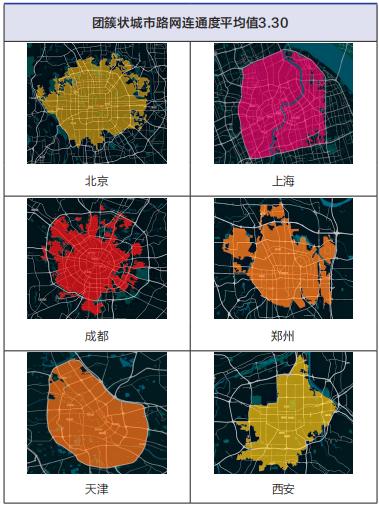
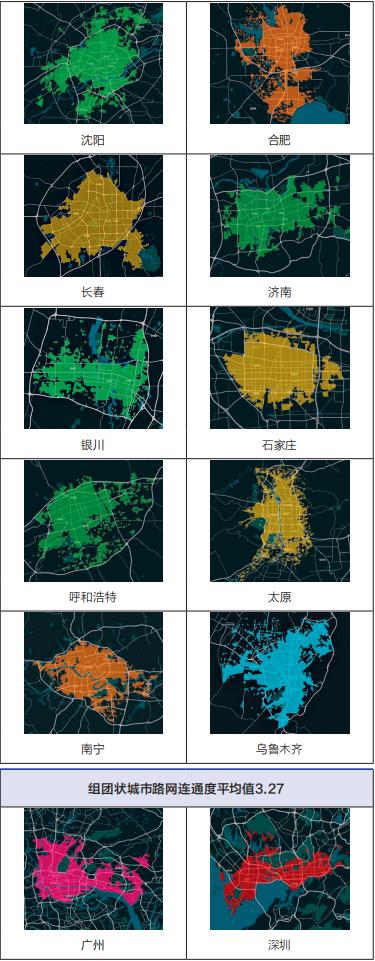
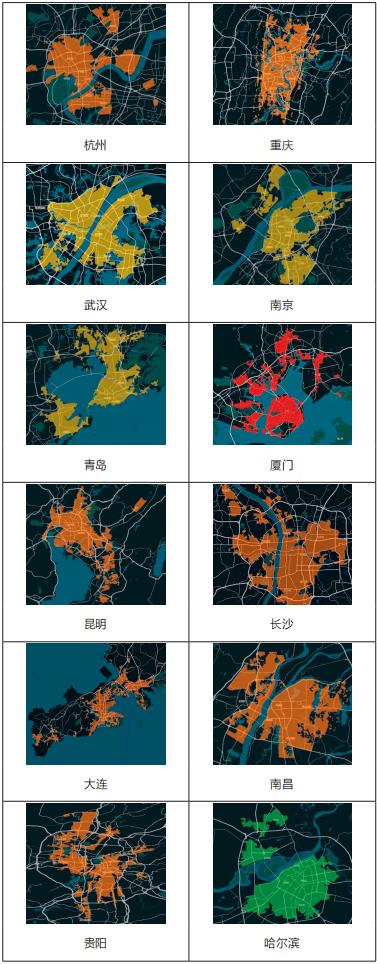
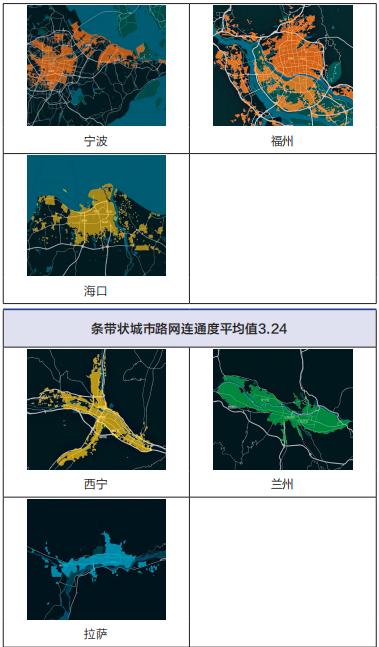
Figure 2 Distribution of Road Network Connectivity in Different Cities
IV. Summary and Prospect
The connectivity of urban road network is one of the indicators to reflect the accessibility of road network and test the rationality of road network structure. Based on the geographic information data, this paper calculates the connectivity of urban road network in 36 key cities in China. The relevant data results can truly reflect the current situation of road network connectivity in big cities in China, which can be used as relevant indicators for urban road network structure evaluation and provide corresponding reference for urban traffic management, urban planning and construction and other fields. (Author: Road Traffic Safety Research Center of the Ministry of Public Security)
This article was published in the 12th issue of Road Traffic Management in 2022.

Audit: Li Xiuju/Li Jiaxin
Editor: Zhao Man
—submission email—
dljtgl120@126.com dljtgl122@126.com
Original title: Frontier of Science and Technology | Analysis on the Index of Holographic Portrait of Road Network Structure for 36 Major Cities in China-Urban Road Network Connectivity